In the world of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are common choices. They may seem similar, but each of them brings own superpowers and quirks to the table.
In this article, we'll delve into the world of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Discover the secrets of how they work and find the best one for your IoT needs.
Bluetooth for IoT Devices
How Bluetooth Works
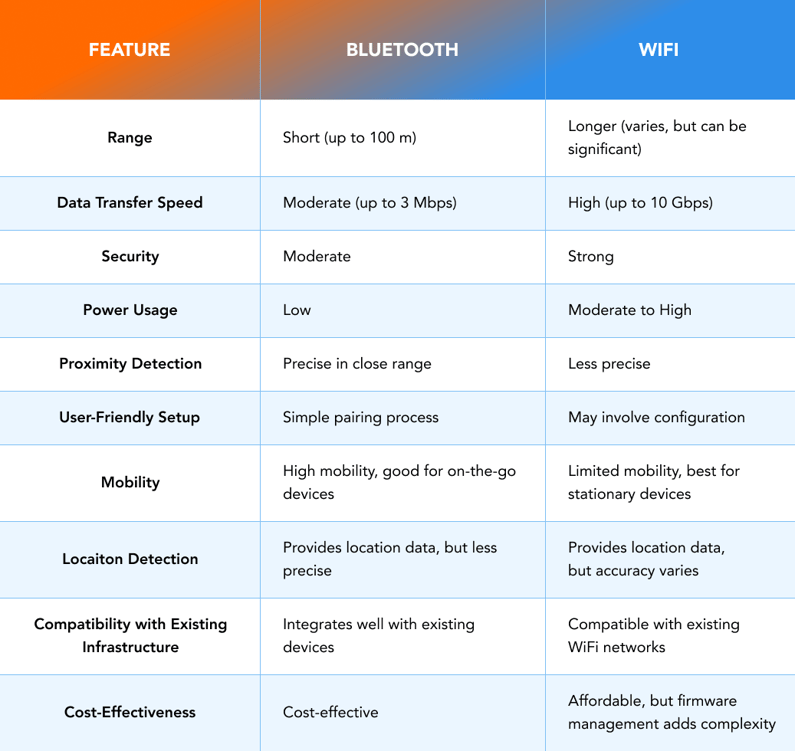
Bluetooth is a wireless technology that forms connections between devices in proximity, typically without requiring a password. It operates on radio frequencies within the 2.4 GHz spectrum. Bluetooth has a range of 1 meter to 1 kilometer, depending on the device and situation. It is mainly used for close-range communication.
Compatibility Requirements
To use Bluetooth, an Internet of Things device needs a microprocessor that can handle Bluetooth technology and another device for paring. Bluetooth offers two commonly used versions for IoT devices: Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). The last one is energy-efficient and suitable for devices with low power requirements.
Bluetooth Features for IoT Devices
Data Transfer Speed
Bluetooth offers a maximum data transfer rate of approximately 3 Mbps (megabits per second). This speed is suitable for tasks like sending sensor data and basic commands. However it may not be ideal for applications requiring rapid transfer of large files or high-definition video streaming.
Bluetooth prioritizes energy efficiency and shorter-range communication over ultra-fast data speeds. This makes it better suited for IoT devices that emphasize conserving power and maintaining reliable connections in proximity.
Security and Privacy
Bluetooth provides a reasonable level of security, but it's important to note that it's not intended as a fully secure protocol. However, it offers some advantages, especially in specific use cases. Since Bluetooth needs physical proximity to start a signal, so it has fewer ways for attacks than an unsecured Wi-Fi network.
Power Usage
One of Bluetooth's standout features is its energy efficiency. It's designed to use significantly less power than Wi-Fi, making it an excellent choice for IoT devices that operate on batteries. This feature extends the battery life of devices, allowing them to function for extended periods without frequent battery replacements.
Range
Bluetooth's range is relatively limited, especially when compared to Wi-Fi. Class 1 Bluetooth devices are typically designed with a maximum range extending up to 100 meters (approximately 328 feet). However, most consumer Bluetooth devices have a range less than this – often just around 10 meters (33 feet). Remember that obstacles and the density of walls between the two devices can influence the actual range.
Proximity Detection
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is renowned for its precise proximity detection capabilities. While it may not provide pinpoint accuracy within inches, it can offer reasonably accurate proximity estimates within dozens of feet. This makes BLE an excellent choice for applications that require close-range interaction or tracking.
User-friendly setup
Bluetooth provides the possibility of a uniform onboarding procedure suitable for all devices and scenarios. Pairing devices through Bluetooth is generally a straightforward process, which can enhance the user experience. However, the ease of onboarding can depend on the specific application and the level of user interaction required.
Mobility
Despite its shorter range compared to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth is a more mobile technology. IoT devices equipped with Bluetooth can move remotely and reconnect to a hub or gateway when possible. This is particularly helpful in situations where devices need to remain connected while in motion. For example, it can be used to track items in a warehouse or monitor patients in a hospital.
Location Detection
Bluetooth can provide location information with a reasonable degree of accuracy. Bluetooth may not be as precise as advanced positioning technologies. However, it can provide location information for tasks like guiding people indoors or tracking items in a small area.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Bluetooth often integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructure. It can connect to devices, such as smartphones and laptops, without requiring additional hardware in most cases. This compatibility makes it a flexible option for IoT solutions that need to interact with different devices already in use.
Cost-Effectiveness
Implementing Bluetooth technology is often cost-effective. Bluetooth modules are readily available and can be integrated into IoT devices without significant added expenses. This affordability makes Bluetooth an attractive choice for IoT projects with budget constraints.
Wi-Fi for IoT Devices
How Wi-Fi Works
Wi-Fi stands for "Wireless Fidelity". It is a wireless technology that enables devices to connect to the internet and communicate with each other without physical cables. It uses radio waves in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Wi-Fi devices, like smartphones and laptops, connect to a central router or access point, allowing data to be transmitted wirelessly. Wi-Fi networks provide internet access and support multiple devices within their coverage area.
Compatibility Requirements
To incorporate Wi-Fi into an Internet of Things device, the device requires a microchip with Wi-Fi capabilities. While obtaining such microchips is relatively easy and cost-effective, practical implementation involves firmware management of the device's Wi-Fi credentials. This is crucial because Wi-Fi networks can be vulnerable to malicious actors if not properly secured.
Wi-Fi Features for IoT Devices
Data Transfer Speed
One of Wi-Fi's standout features is its impressive data transfer speed. Wi-Fi offers a maximum theoretical speed that is much faster than Bluetooth, reaching nearly 10 Gbps. This makes Wi-Fi the preferred choice for applications that involve transferring large data files, such as videos, images, or extensive datasets.
Security and Privacy
Wi-Fi provides robust security features, making it an excellent choice when dealing with sensitive data transmission. It supports various security protocols, including WEP, WPA, WPA2, and the latest and preferred version, WPA3. These protocols add layers of protection to Wi-Fi networks, making them more secure against potential threats.
Power Usage
While Wi-Fi excels in data transfer speed and range, it tends to consume more power compared to Bluetooth. IoT devices using Wi-Fi may require a direct power source or larger batteries to sustain continuous operation. This power consumption factor is important to consider, especially for battery-powered devices.
Range
Wi-Fi network range vary depending on factors such as frequency, transmission power, antenna type, and the environment. In general, Wi-Fi networks have the potential to cover larger areas compared to Bluetooth. This extended range is particularly advantageous for IoT applications that require connectivity over more extensive spaces.
Proximity Detection
While Wi-Fi isn't primarily for detecting how close things are, it can kind of do it. It estimates the distance between a device and an access point using strength. However, Bluetooth is more accurate for proximity in specific situations.
User-friendly setup
Setting up Wi-Fi connections on IoT devices can sometimes be more complex than pairing devices through Bluetooth. Wi-Fi onboarding may involve configuring network settings, including SSID and password input. This complexity can lead to challenges in user onboarding, particularly in scenarios where users need to connect devices themselves.
Mobility
Wi-Fi networks are typically limited to the location where they were set up. While wirelessly connected IoT devices can move within Wi-Fi access point range, they lack the mobility that Bluetooth devices offer. In situations where devices need to maintain connections while in transit, Wi-Fi may present limitations.
Location Detection
Wi-Fi can give location information, but its accuracy depends on a number of access points, the signal strength, and the environment. In some cases, Wi-Fi-based location detection may be less accurate than specialized positioning technologies.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
One significant advantage of Wi-Fi is its compatibility with existing infrastructure. Wi-Fi networks are prevalent, especially in urban and commercial environments. IoT devices equipped with Wi-Fi can easily connect to these existing networks, simplifying deployment and integration.
Cost-Effectiveness
Using Wi-Fi on an IoT device typically necessitates the availability of a microchip, which is commonly accessible and budget-friendly. However, making Wi-Fi work also means dealing with the device's Wi-Fi settings in the firmware. This can make things more complex and costly while developing and maintaining the device.
Choosing Between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for IoT
When deciding between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for IoT, there's no one-size-fits-all answer. Your choice should align with your specific business needs, priorities, and the intended use of the IoT device.
Remember that usually, an IoT device can't use just Bluetooth. It needs another device like Wi-Fi or cellular to send data.
In general, Bluetooth is ideal for mobile devices with low power requirements, close-range interactions, and scenarios where mobility is essential. Wi-Fi is beneficial for large stationary devices. These devices require fast data transfer and work over large areas. Additionally, they can connect to existing Wi-Fi networks.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your unique circumstances. Consider consulting with an IoT development expert to make the best connectivity decision for your product. To make the right decision for your IoT project, carefully consider your needs, compare the pros and cons of each technology, and choose the one that fits your IoT goals best.

