Not every organization can rely on public networks to keep things running. In places where performance, privacy, and reliability really matter, like busy ports, production lines, hospitals, or university campuses, a shared network often falls short. That’s why more and more businesses are turning to Private LTE, a solution that gives them full control over their connectivity.
Private LTE isn’t just a trend. It’s a powerful way to build a secure, fast, and flexible network that works exactly how and where you need it. From factories full of connected machines to rural areas that public carriers skip, this technology is changing the way industries stay connected.
Before we dive in, here’s what this guide covers:
What’s Inside:
- The Growing Importance of Private LTE Networks
- What is a Private LTE Network?
- Types of Private Cellular Networks
- Network Deployment Models
- Private Network Frequency Bands
- Private Network Applications
- POND IoT Private LTE and NaaS Services
The Growing Importance of Private LTE Networks
Across industries, the need for private, high-performance connectivity is becoming hard to ignore. Public networks often fall short when control, security, or reliability are critical. That’s why more companies are turning to Private LTE, a solution that puts them in charge of their own network infrastructure.
According to recent research, global spending on private LTE and 5G infrastructure is expected to reach $6.4 billion by the end of 2026. Much of this growth is being driven by sectors like manufacturing, logistics, energy, and healthcare, where digital transformation and automation demand strong, secure, and stable connectivity. (Source: GlobeNewswire – Global CBRS, Private LTE & 5G Networks Report)
A big part of what’s made private LTE more accessible in the United States is the CBRS spectrum. CBRS, which operates in the 3.5 GHz band, allows enterprises to use shared mid-band spectrum without needing to buy exclusive licenses. This helps businesses launch private networks at a much lower cost, while still getting strong indoor and outdoor coverage. (Source: PrivateLTEand5G.com – Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) – Everything You Want to Know)
Globally, the number of private LTE and 5G networks is growing rapidly. According to Berg Insight, that number is expected to reach 23,600 by 2029, up from 4,700 at the end of 2024. This growth, driven by a 38 percent compound annual growth rate, reflects how essential private networks are becoming for industries focused on automation, security, and reliable performance. (Source: Berg Insight – Private LTE & 5G Network Market)
Private LTE is often the first step. Many organizations start with LTE now, then layer in 5G capabilities as their needs for speed, automation, or data processing grow.
What is a Private LTE Network?
It is a private cellular system built specifically for one organization. Unlike public mobile networks that serve countless users and are run by major carriers, this kind of setup gives the organization complete control. It runs independently, stays secure, and is built to deliver reliable coverage in places where steady connectivity truly matters.
One key difference is how it uses its own slice of wireless spectrum. Since that spectrum is not shared with the public, the network avoids the slowdowns and interruptions that can happen in busy areas. This also allows the organization to adjust the network to fit the needs of different locations, devices, or workflows.
Because the bandwidth is reserved, the most important systems can always come first. Things like safety equipment, automated machines, or on-site monitoring tools can keep working without lag. That makes real-time data sharing and fast communication possible when it matters most.
Privacy is also a major reason organizations choose this type of network. It can be set up with strict access rules, strong encryption, and other protections that keep sensitive data safe. Everything stays inside the company’s own system, without relying on third-party infrastructure. This makes it a strong choice for industries where security is a top priority.
Whether it’s set up in a manufacturing plant, an airport, a hospital, or across a university campus, this kind of network gives teams the flexibility, reliability, and peace of mind they often cannot get from public networks.
Types of Private Cellular Networks
Private cellular networks are typically built using either 4G LTE or 5G technology. Both options give businesses their own wireless network that is not shared with the public, but there are differences in what each one can offer.
Private LTE (4G) Networks
These networks use LTE, the same standard that powers most 4G services around the world. Organizations choose private LTE because it is dependable, widely supported, and works well for a variety of applications. It offers solid data speeds, low delay, and the ability to handle many connected devices at once. For companies that need better coverage, more control, and greater security than what public networks provide, private LTE has become a popular choice.
Private 5G Networks
Private 5G is built on newer wireless technology that brings even more to the table. It supports faster connections, less delay, and many more devices on the same network. One feature that makes 5G unique is something called network slicing. This lets a company create different virtual networks within the same physical system, each with its own settings based on what it’s used for. For example, one slice might be used to control machines in real time, while another handles cameras or sensors that send data in the background.
While 5G introduces some advanced capabilities, it doesn’t replace LTE. Many organizations begin with LTE and move to 5G later, depending on what their business needs and devices require.
Network Deployment Models
Private cellular networks can be set up in different ways depending on how much control an organization wants and whether it prefers to use existing infrastructure or build everything from scratch. There are three main approaches to choose from:
Standalone Network (NPN)
This model gives the organization complete control. All the network equipment, such as radios, servers, and software, is owned and managed by the business itself. Nothing depends on a public mobile operator. Because everything runs on a private system, it offers the highest level of customization, security, and independence.
Public Network-Integrated (NPN-i)
In this setup, a mobile operator provides a separate part of its public network to the organization. This is often called a “network slice.” The company still gets a private and secure connection, but it uses the operator’s existing infrastructure. This model is useful for businesses that want some level of control and performance guarantees without having to manage the entire network.
Hybrid Network
A hybrid network combines elements from both standalone and public-integrated models. A company might own part of the infrastructure, like indoor equipment for a facility, while relying on a mobile operator to provide service for outdoor or remote locations. This approach offers more flexibility and can be adjusted based on geography, cost, or specific use cases.
Each model comes with its own balance of control, cost, and complexity. The best fit depends on what the organization needs and how much it wants to manage on its own.
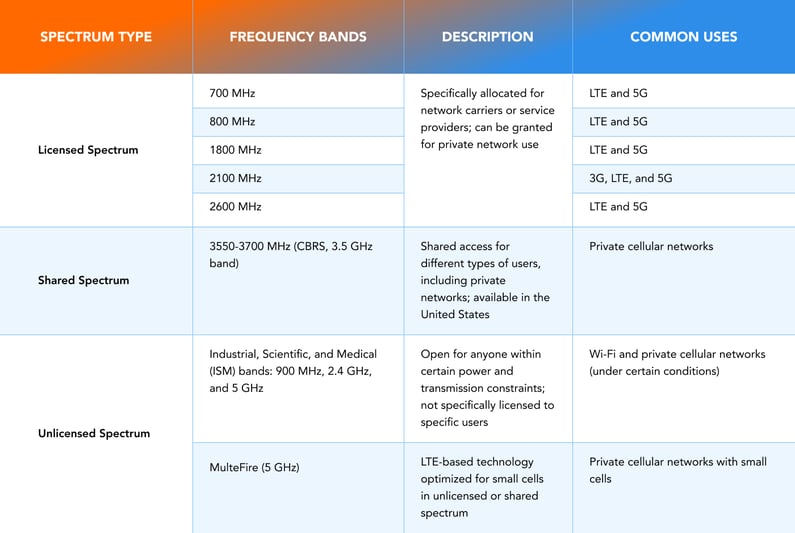
Private Network Frequency Bands
Private networks rely on radio spectrum to operate, but not all spectrum works the same. Some frequencies travel far and penetrate buildings easily, while others offer faster data but only across shorter distances. Understanding these differences is key to building a network that actually fits your location and use case.
Low-Band (Below 1 GHz)
This band is all about reach. It covers long distances and handles obstacles like walls, trees, or vehicles better than other ranges. That makes it a solid choice for wide areas—think remote farms, utility sites, or large campuses. It won’t deliver blazing speeds, but it keeps you connected when range matters most. Common examples include the 700 MHz and 800 MHz bands used in LTE and 5G.
Mid-Band (1 to 6 GHz)
Mid-band strikes a solid middle ground. It gives you good speed and decent coverage at the same time, making it a favorite for ports, logistics hubs, and manufacturing zones. Frequencies like 1800 MHz, 2100 MHz, and 2600 MHz are popular here. In the U.S., the 3.5 GHz CBRS band is gaining traction. It offers strong performance without requiring businesses to buy expensive exclusive licenses, opening the door for more private network deployments.
High-Band (Above 6 GHz)
Also known as millimeter wave, this band offers extremely fast speeds and ultra-low latency. It's a great fit for real-time applications, like automated robotics or advanced surveillance systems, but it has a very short range. Signals in this band are easily blocked and can’t travel far, so companies need more antennas to keep everything connected.
There are also different ways to access these frequencies, depending on your needs and budget:
- Licensed spectrum is fully controlled by whoever holds the license. It’s reliable and secure, but often expensive and regulated.
- Shared spectrum, like CBRS, is designed to let different users operate in the same space without stepping on each other. It’s flexible and cost-effective for enterprises.
- Unlicensed spectrum is open to everyone, as long as you play by the technical rules. Bands like 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5 GHz fall into this group.
Private Network Applications
Private LTE networks are proving valuable across a wide range of industries. Their ability to provide secure, reliable, and dedicated connectivity makes them ideal for operations where public networks can’t deliver consistent performance.
Enterprises
Companies can create custom networks across offices, campuses, or industrial parks. This improves internal communications, supports secure data transfer, and powers tools like high-quality video conferencing and cloud-based collaboration.
Industrial IoT
Factories, warehouses, and logistics hubs rely on connected machines, sensors, and systems. Private LTE enables real-time data exchange, automation, and predictive maintenance. Companies like BMW and Airbus already use it to support robotics and production lines.
Smart Cities
Cities are using private networks to manage traffic lights, monitor public utilities, reduce waste, and improve safety. With dedicated connectivity, municipal services can react faster and operate more efficiently.
Public Safety
Emergency responders and disaster teams need secure, always-on communication. Private LTE gives them a dedicated channel that stays online when public networks are overloaded or unavailable.
Remote Worksites
Mines, oil fields, and offshore platforms need strong, secure connections far from urban centers. Private LTE enables asset tracking, operational monitoring, and worker safety systems in places where public signals can’t reach.
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics benefit from fast, private connections that support patient monitoring, secure records access, and team communication. These networks help medical devices, staff tablets, and back-end systems work together without delays.
Education
Universities and K-12 campuses can use private LTE to provide reliable, high-speed access across classrooms, labs, and dorms. It supports online learning, shared resources, and video tools—even when many students are online at once.
Events and Pop-Up Sites
Concerts, sports venues, and temporary field offices can deploy private LTE to meet short-term needs. These networks handle spikes in demand and ensure seamless communication and service delivery during high-traffic moments.
Maritime and Aviation
Ships, ports, and airports use private networks to improve safety, automate operations, and connect systems like baggage tracking, logistics platforms, and ground crews. For example, Miami International Airport uses private LTE to coordinate staff, track luggage, and manage vehicles.
Rural and Remote Areas
Many communities lack strong public coverage. Private LTE can fill the gap, supporting local healthcare clinics, schools, and small businesses. It brings reliable access to vital services and opens doors to digital tools once out of reach.
POND IoT Private LTE and NaaS Services
If you're looking to build your own private LTE network without managing everything yourself, our Network as a Service (NaaS) solution gives you exactly that. We handle the infrastructure while you stay in control of how your network runs.
With POND IoT, you get a secure and reliable setup designed to keep your business connected, even during network outages. Our service includes built-in redundancy, strong data protection, and the flexibility to support a wide range of use cases, from factories to hospitals and remote sites.
You don’t need to invest in hardware or hire a dedicated team. We provide the support, and visibility you need to run a private network tailored to your business.
Need reliable internet as a backup? Explore our Internet Failover plans to keep your operations running without interruption.
Let’s talk about how we can help you deploy your own private LTE network without the complexity.

