In the rapidly evolving world of the Internet of Things (IoT), reliable connectivity and secure data transmission are paramount. To do this, businesses and people often use three important technologies: APNs, VPNs, and Static IPs. In this blog post, we will explain what these are, how they work, and why they are important for successful IoT deployments.
What is an Access Point Name (APN)?
An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a cellular network and other public or private networks. It acts as a bridge, allowing IoT devices to communicate with external servers, cloud platforms, and the Internet. Each device connected to a cellular network requires a unique Access Point Name, which the cellular service provider usually assigns.
How do APNs work?
When an IoT device attempts to access external resources, it sends data to the cellular network. The APN provided by the network operator then routes this data to the destination server or service. This process ensures seamless and secure communication between devices and the external world.
Why use APNs for IoT deployments?
- Security: This technology provides a layer of security by acting as a buffer between the public Internet and the devices. This helps in protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Network Management: APNs allow network operators to manage and prioritize data traffic efficiently, ensuring smooth communication even in congested areas.
- Roaming Capabilities: For devices deployed across different regions or countries, Access Point Names promote seamless roaming between various cellular networks.
The different types of APNs
Access Point Names come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs and requirements in IoT deployments. Let's explore the different types of APNs and the benefits they offer:
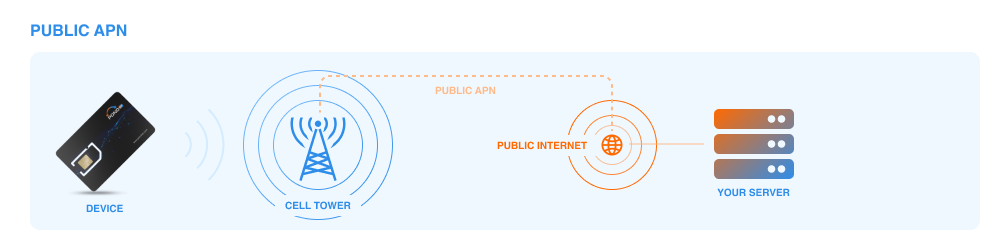
Public APNs
Public APNs are ideal for IoT deployments that involve devices communicating with services and servers over the public Internet. They connect devices to the Internet, making it easy for them to access cloud platforms, web services, and public APIs. Public Access Point Names are widely available and easily accessible, making them suitable for most IoT applications.
Private APNs:
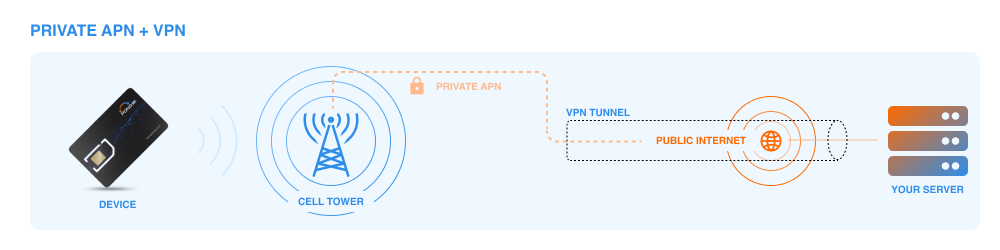
In contrast to public APNs, private APNs create a closed and secure network environment for IoT devices. These APNs are especially useful in scenarios where data privacy and security are top priorities. Companies frequently use private APNs in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) deployments to safeguard sensitive data and critical operations against cyber threats. By operating within a private network, communication between devices and servers remains restricted, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Carrier-Managed APNs:
Cellular network operators provide and maintain carrier-managed APNs. These APNs make IoT deployments simpler and more convenient by having the network operator handle APN configuration and management. Organizations that want to avoid the technical challenges of setting up an APN should use carrier-managed APNs. This option guarantees a reliable and seamless connection for their devices.
Custom APNs:
Custom APNs provide a high degree of flexibility and customization options for IoT deployments. Organizations can tailor the APN settings to suit their specific network requirements, allowing for optimized data routing and performance. Custom APNs are useful for big IoT projects. They help improve efficiency, reduce latency, and enhance overall performance by adjusting network parameters.
Roaming APNs:
Roaming APNs enable IoT devices to maintain connectivity and communication across different cellular networks and geographic regions seamlessly. When devices move between different network operators, roaming APNs switch to the right network, ensuring uninterrupted data transmission. This capability is essential for global IoT deployments where devices may traverse national borders or areas with varying network coverage.
What is a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
A VPN allows devices to connect to the Internet as if they were on a private network. This is possible even though they are actually on a public network. VPNs create a secure tunnel between the device and the target server, encrypting all data transmitted through it.
How VPNs work
When an IoT device connects to a VPN, it establishes a connection with a VPN server. The devices and server encrypt data, so unauthorized parties can't understand it, even if they intercept it. The VPN server then forwards the data to its intended destination on the Internet.
Why use VPNs for IoT deployments?
- Enhanced Security: VPNs provide end-to-end encryption, safeguarding sensitive data and preventing potential cyber threats.
- Geo-spoofing: VPNs enable users to make a device appear in a different location. This feature can help bypass restrictions or regulations that rely on location.
- Remote Access: VPNs enable secure remote access to devices and networks, promoting efficient management and troubleshooting.
Understanding the Integration of Private APNs and VPNs in IoT Security
When delving into the realm of IoT security, understanding how private Access Point Names (APNs) and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) work together is crucial. These technologies each play a distinct role in protecting data as it moves from IoT devices to the internet.
The Role of VPNs in IoT
A VPN further elevates the security setup by creating a secure tunnel through which the data transmitted from IoT devices travels encrypted. Implementing a VPN can occur at various levels:
Device Level: Software-based VPNs on each IoT device ensure end-to-end encryption right from the device itself.
Gateway Level: A VPN can also be implemented at the gateway level that aggregates data from multiple devices, offering encryption as data moves to the main server.
How They Work Together
In an IoT deployment, private APNs funnel device connections through a secure, designated route, minimizing exposure to the vulnerabilities of the public internet. A VPN complementarily encrypts this data across the transmission, adding an additional layer of security through encryption.
Firstly, the IoT devices connect through the private APN, ensuring they are using a secure and isolated path to the internet.
Secondly, the VPN encrypts the data being transmitted over this path, guarding against interception and ensuring that even if data is somehow captured, it remains unreadable.
Choosing the Right Security Setup
Not all IoT deployments will require the added security of a VPN, though the complexity and security needs of the project might necessitate it. The decision fundamentally hinges on a detailed risk analysis and understanding the specific security requirements of the IoT application in question. Collaborating with your connectivity provider can help pinpoint the most tailored and secure setup for your deployment.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a VPN for IoT Devices
Selecting the right VPN for your IoT devices involves several crucial considerations that can impact security, functionality, and overall network performance. Here are the primary factors to think about:
- Necessity of VPN Based on Use Case
- Complexity and Cost
- Flexibility Versus Security
- Security Features
- Data Protection and Encryption
- Confidentiality and Privacy Assurance
Choosing the right VPN for IoT devices is a balance between enhanced security and the potential drawbacks of increased cost and complexity. By carefully considering these factors, organizations can ensure they select a VPN solution that not only secures their devices but also aligns with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
What is a Static IP Address?
A Static IP Address is a fixed and unchanging numeric label assigned to an device connected to a network. In contrast, Dynamic IP addresses change each time a device connects to the network. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) typically provide static IPs, which remain constant throughout the device's connection.
How Static IPs work
When an IoT device connects to a network, the network assigns it an IP address, either statically or dynamically. In the case of Static IPs, the device retains the same address whenever it connects to the network. This permanence is beneficial for services or applications that require constant access to the device, such as remote monitoring or control.
Why use Static IPs for IoT deployments
Device Accessibility: Static IPs make it easy to connect and manage IoT devices remotely, as they always have the same address.
- Server Hosting: For IoT applications on a device, a Static IP is necessary for reliable access. This is particularly important when services are publicly available online.
- Security and Authorization: Static IPs improve security by only allowing connections from authorized sources and limiting access to specific devices or networks.
In conclusion, APNs, VPNs, and Static IPs play a vital role in optimizing IoT deployments. APNs facilitate seamless communication between devices and external networks, while VPNs ensure secure and encrypted data transmission. On the other hand, Static IPs provide a stable and reliable point of access for managing IoT devices.
With these technologies, businesses and individuals can safeguard sensitive data, enhance network performance, and streamline remote device management. Embracing these tools empowers organizations to embrace the full potential of IoT while maintaining a robust and secure infrastructure.

